
new cells are produced from existing cells
cells are the basic unit of structure & function of all living things And in 1855, Rudolph Virchow, a German doctor, asserted that all cells must come from other cells by the process of cell division.Ĭell Theory (based on 200+ years of discoveries) One year later, a German zoologist by the name of Theodor Schwaan postulated that animals are also composed of cells. In 1838, Dutch botanist Matthias Schleiden concluded that all plants are composed of cells.
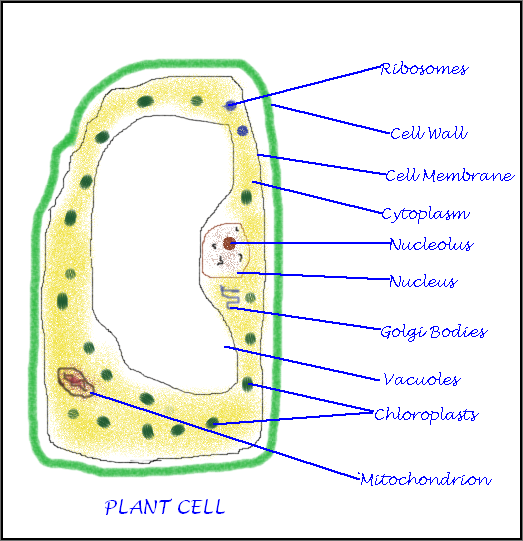
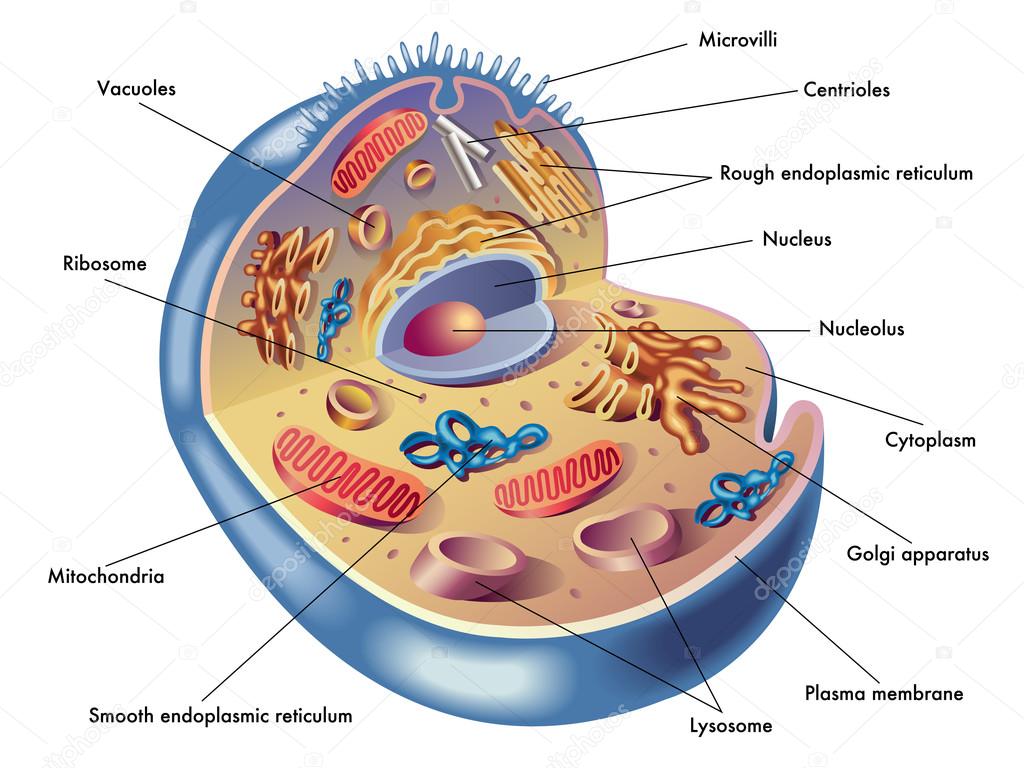
In the mid-19th century, three different scientists working separately each published important conclusions about cells. Leeuwenhoek (1675), a Dutch lens maker: microscope, in the 150 years after his work, microscope lenses improved and scientists were able to observe and understand more parts of the cell. Hooke (1665), an English scientist: cell Cell structure is correlated to cellular function. The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live. Introduction Overview: The Importance of Cells (h) use the knowledge gained in this section in new situations or to solve related problems. 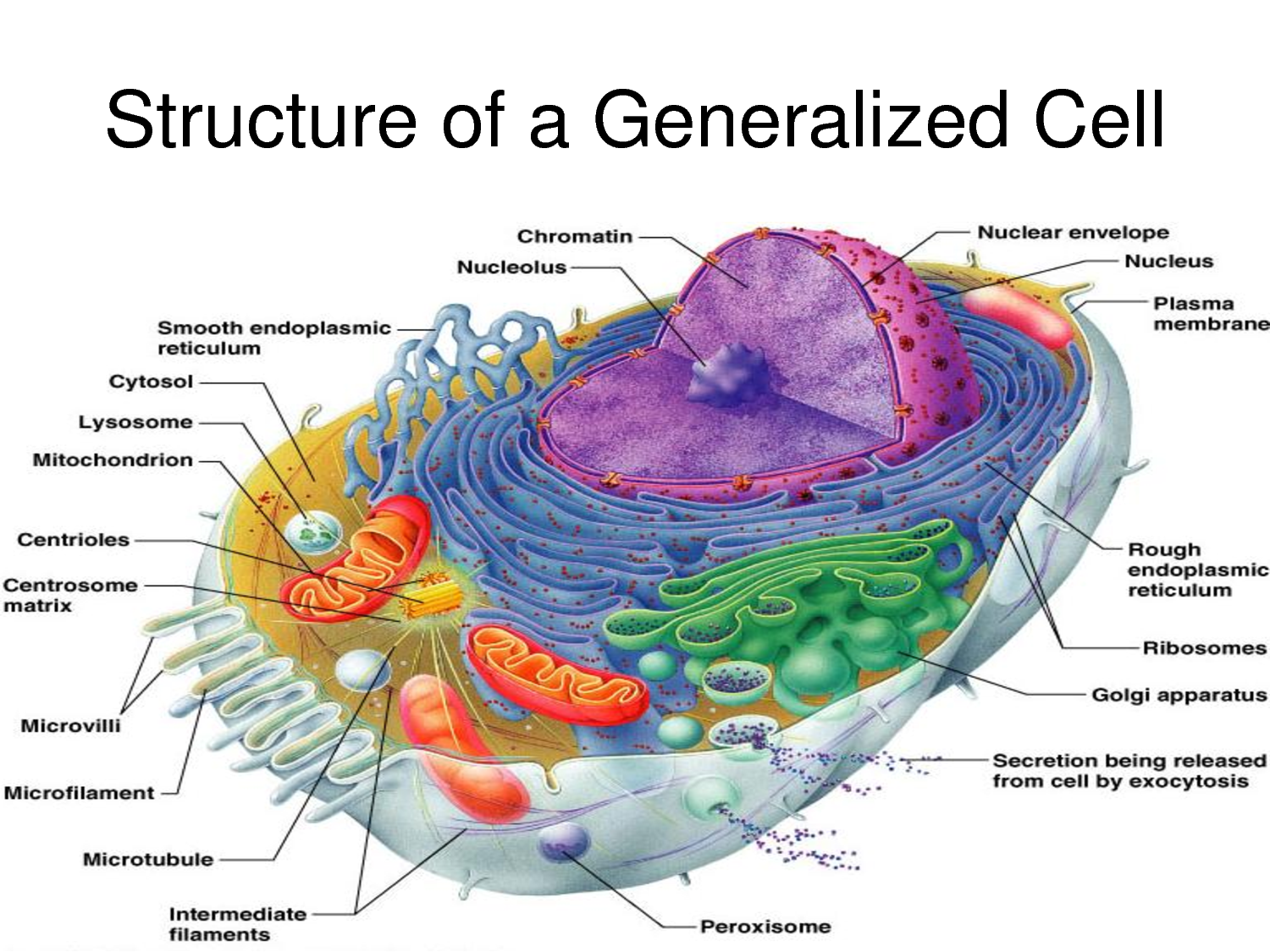 (g) describe the structure of a prokaryotic cell and compare and contrast the structure of prokaryotic cells with eukaryotic cells. (f) draw and label low power diagrams of tissues (including a transverse section of a stems, roots, and leaves) and calculate the linear magnification of drawings. (e) compare and contrast the structure of typical animal and plant cells. (d) outline the functions of the membrane systems and organelles listed in (c). (c) describe and interpret drawings and photographs of typical animal and plant cells, as seen under the electron microscope, recognising the following membrane systems and organelles: rough and smooth endoplasmic reticula, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, ribosomes, lysosomes, chloroplasts, plasma/cell surface membrane, nuclear envelope, centrioles, nucleus and nucleolus. (b) explain and distinguish between resolution and magnification, with reference to light microscopy and electron microscopy. (a) use an eyepice graticule and stage micrometer to measure cells and be familiar with units (millimetre, micrometre, nanometre) used in cell studies.
(g) describe the structure of a prokaryotic cell and compare and contrast the structure of prokaryotic cells with eukaryotic cells. (f) draw and label low power diagrams of tissues (including a transverse section of a stems, roots, and leaves) and calculate the linear magnification of drawings. (e) compare and contrast the structure of typical animal and plant cells. (d) outline the functions of the membrane systems and organelles listed in (c). (c) describe and interpret drawings and photographs of typical animal and plant cells, as seen under the electron microscope, recognising the following membrane systems and organelles: rough and smooth endoplasmic reticula, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, ribosomes, lysosomes, chloroplasts, plasma/cell surface membrane, nuclear envelope, centrioles, nucleus and nucleolus. (b) explain and distinguish between resolution and magnification, with reference to light microscopy and electron microscopy. (a) use an eyepice graticule and stage micrometer to measure cells and be familiar with units (millimetre, micrometre, nanometre) used in cell studies. 
Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to:
Characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Outline functions of organelles in plant and animal cells. Detailed structure of typical animal and plant cells, as seen under the electron microscope. Cells as the basic units of living organisms. CHAPTER 1 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Leonardus, S.Si.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
